What is a network switch?
A network switch connects two or mode devices together so that they can send packets to each other.
Devices that can be connected via switch are:
- computer
- printers
- wireless access points i.e. routers
Diagram:

Switches:
- have many network interfaces/ports
- provides connectivity to hosts within the same LAN (Local Area Network)
- do not provide connectivity between LANs/over the internet.
What is LAN (Local Area Network)?
A local area network (LAN) is a group of connected devices within a close physical proximity.
Example of LAN network is home WIFI networks. Your home wifi connects different devices within your home via switch.
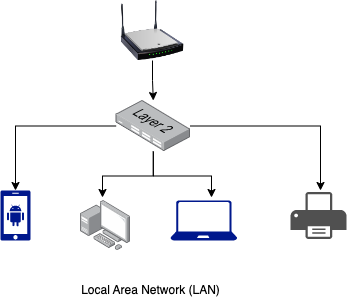
A LAN requires:
- a router
- eithernet cables or a wifi hotspot
- switch
- host devices
There is only one requirement to setup a LAN is that the connected devices are able to send or recieve data.
How network switch function?
Network switches can operate at either:
- Layer-2: OSI or data link layer
- Layer-3: network layer
Layer 2 switch forwards data based on the destination MAC address, while layer 3 switch forwards data based on the destination IP address.
Layer 2 network switches maintain a table in memory to remember which device is connected to which port. Let's take an example to understand:
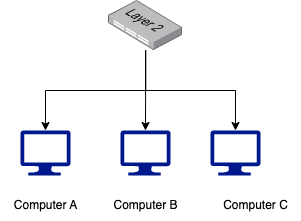
Let say that we have 3 computers which are connected to layer 2 switch. Let's assume that:
- Computer A is connected to Port 1
- Computer B is connected to Port 2
- Computer C is connected to Port 3
We just turned on the switch at this point switch does not know anything about mapping and table is clear.
Here is how memory table look like in the beginning:
| Mac Address | Port |
|---|---|
| ? | ? |
| ? | ? |
| ? | ? |
When switch is turned on it has not created a memory table and it does not know where computer A, B and C is connected. It does not know device mac address.
Let say that computer A sends message to computer B. A message is first recieved by switch and it notes computer A's mac address and connected port.
it then forwards this recieved message to all devices in a network (except computer A) because this is where message came from.
This process is known as "flooding". When computer B replies, it records computer B's mac address and port as well.
| Mac Address | Port |
|---|---|
| Computer A's mac address | 1 |
| Computer B's mac address | 2 |
| ? | ? |
Now, switch CAM table knows where Computer A and Computer B are in a network and it also know their mac address and port where they connected.
Different types of switches:
- KVM Switches
- Managed Switches
- Unmanaged Switches
- Smart Switches
- PoE Switches
- Modular Switches
- LAN Switches